Selector And Rule Config
Features
This document will introduce the use of selectors and rules in the Apache ShenYu background management system. For the concept and design of selectors and rules, please refer to Flow Control.
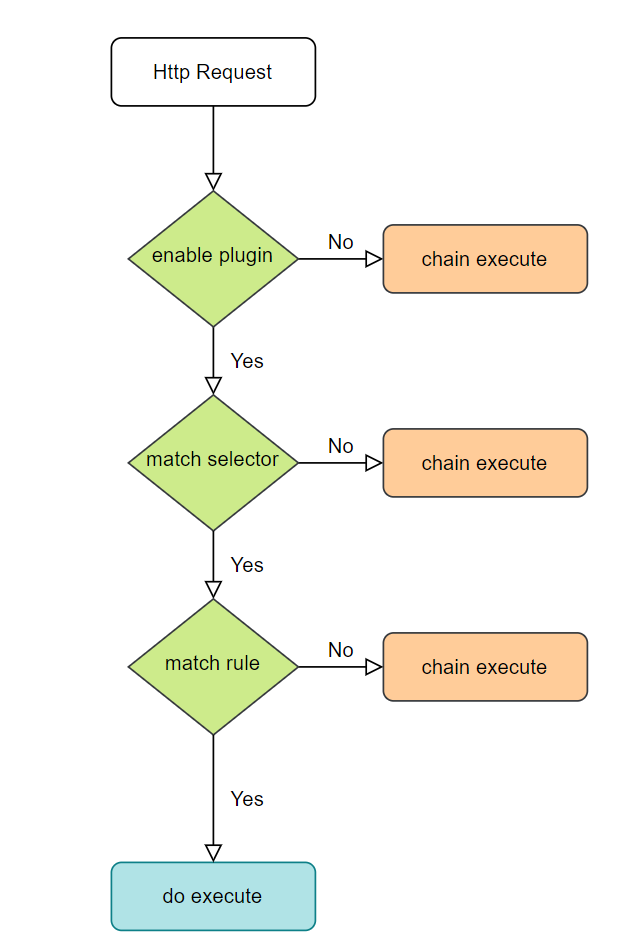
Please refer to the deployment document, choose a way to start shenyu-admin. For example, local deployment. After startup, visit http://localhost:9095, the default username and password are: admin and 123456 .
Selector
All plugins are displayed in the PluginList, and selectors and rules can be added to each plugin:
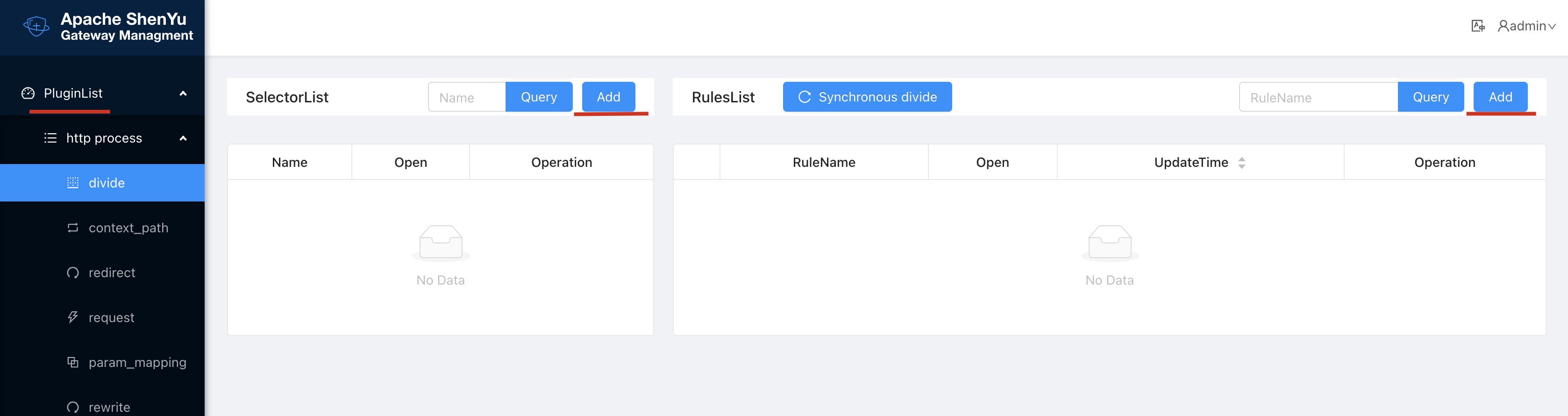
For example, add a selector to the divide plugin:
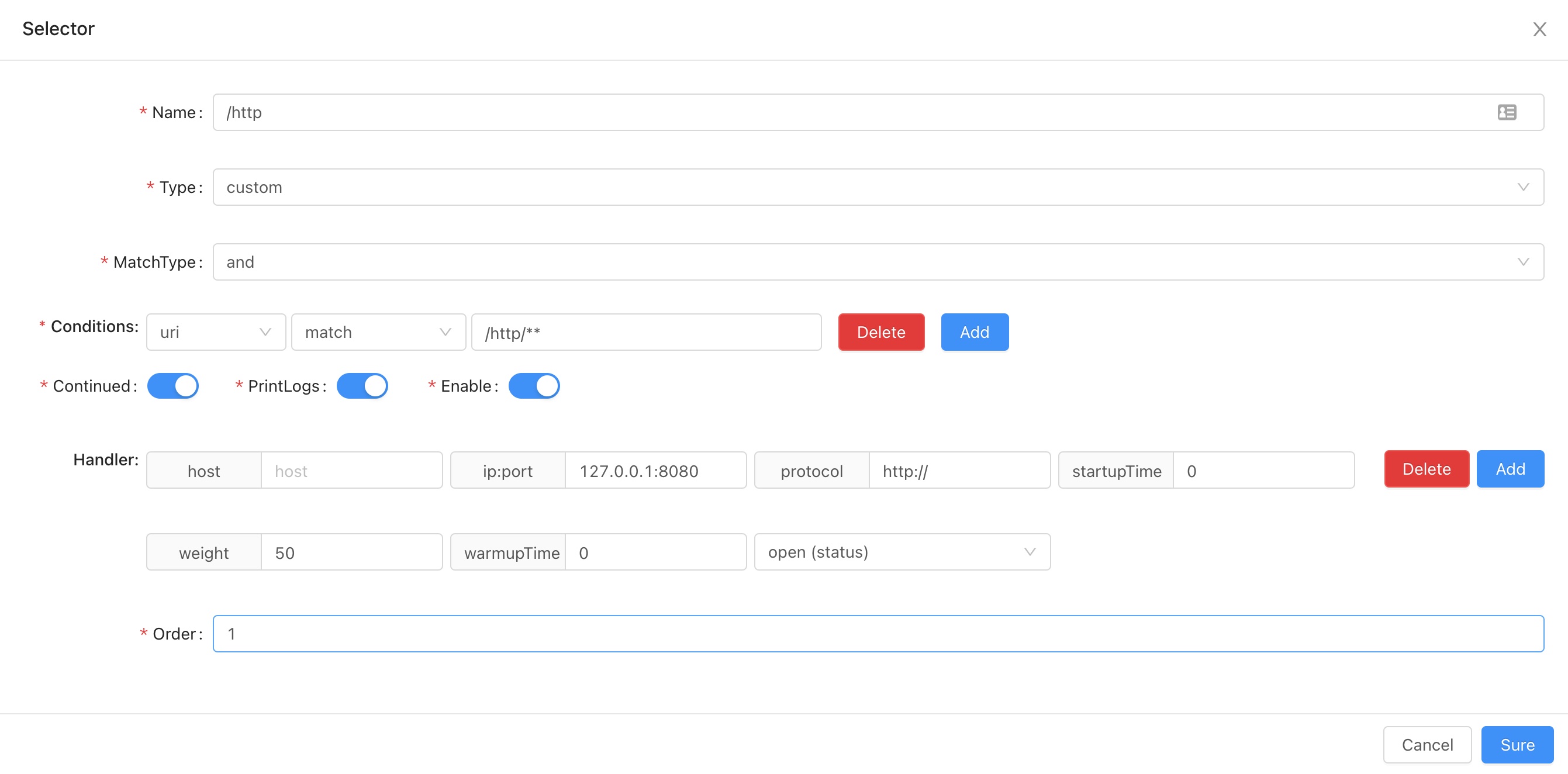
-
selector detailed explanation:
- Name: create your selector with a distinguish name.
- Type: Choose request matching strategy.
custom: Only handle requests that meet the following matching conditions.full: Handle all requests.
- MatchType: Condition combination type.
and: Need to meet all conditions.or: Meet any of the conditions.
- Conditions:
- uri: filter request with uri.
- header: filter request with request header.
- query: filter request with query string.
- ip: filter request with your real ip.
- host: filter request with your real host.
- post: not recommend to use.
- cookie: filter request with cookie.
- req_method: filter request with request method.
- condition match:
- match : fuzzy string matching,recommend to combine with uri,support path-matching.(/test/**).
- = : matches only if they are equal.
- regEx : regex matching,match characters in regex expression.
- contains: when it contains the specified value, it matches.
- TimeBefore: before the specified time.
- TimeAfter: after the specified time.
- exclude: the inverse of the method of
match. - startsWith: when its prefix is equal to the specified value, it matches. In certain scenarios,
matchcan be replaced (such as/test/instead of/test/**) for better performance. - endsWith: when its suffix is equal to the specified value, it matches.
- pathPattern: it's an optimized version of
match, which has better performance thanmatch, but does not support writing**in the middle of the path (such as/api/**/xxx).
- Continued: whether the subsequent selector is still executed.
- PrintLogs: it will print the matching log with the open option enabled.
- Enable: whether to enable the plugin.
- Order:the smaller will have high priority to execute among multi-selectors.
- Handler: The
handlefield, configured in Plugin handle management. Its purpose is to determine the actions to take when the request matches this selector. Within the selector, thehandlefield is often used to represent a manually maintained list of service instances. Each service instance includes the following fields:host: Host addressip:port: IP+port addressprotocol: Protocolweight: Weight of the service instancewarmupTime: Service warm-up timestartupTime: Service startup timestatus: true indicates the service node is available, false indicates it is not available
Note: For plugins that incorporate service discovery modules (such as the Divide plugin, Grpc plugin, and WebSocket plugin), the selector page does not display the handler (i.e., the
handlefield). Instead, it is manually managed through theService Discoverytab under local mode. See Discovery Module for details.
- the above picture means: when the prefix of the request uri is
/http, it will redirect to this service127.0.0.1:8080. - selector advice : combine
uricondition andstartsWithprefix(/contextPath/)as the first request filter. - selector(the same for rule) match condition fuzzy string matching rule:
?matches one character*matches zero or more characters**matches zero or more directories in a path
Rule
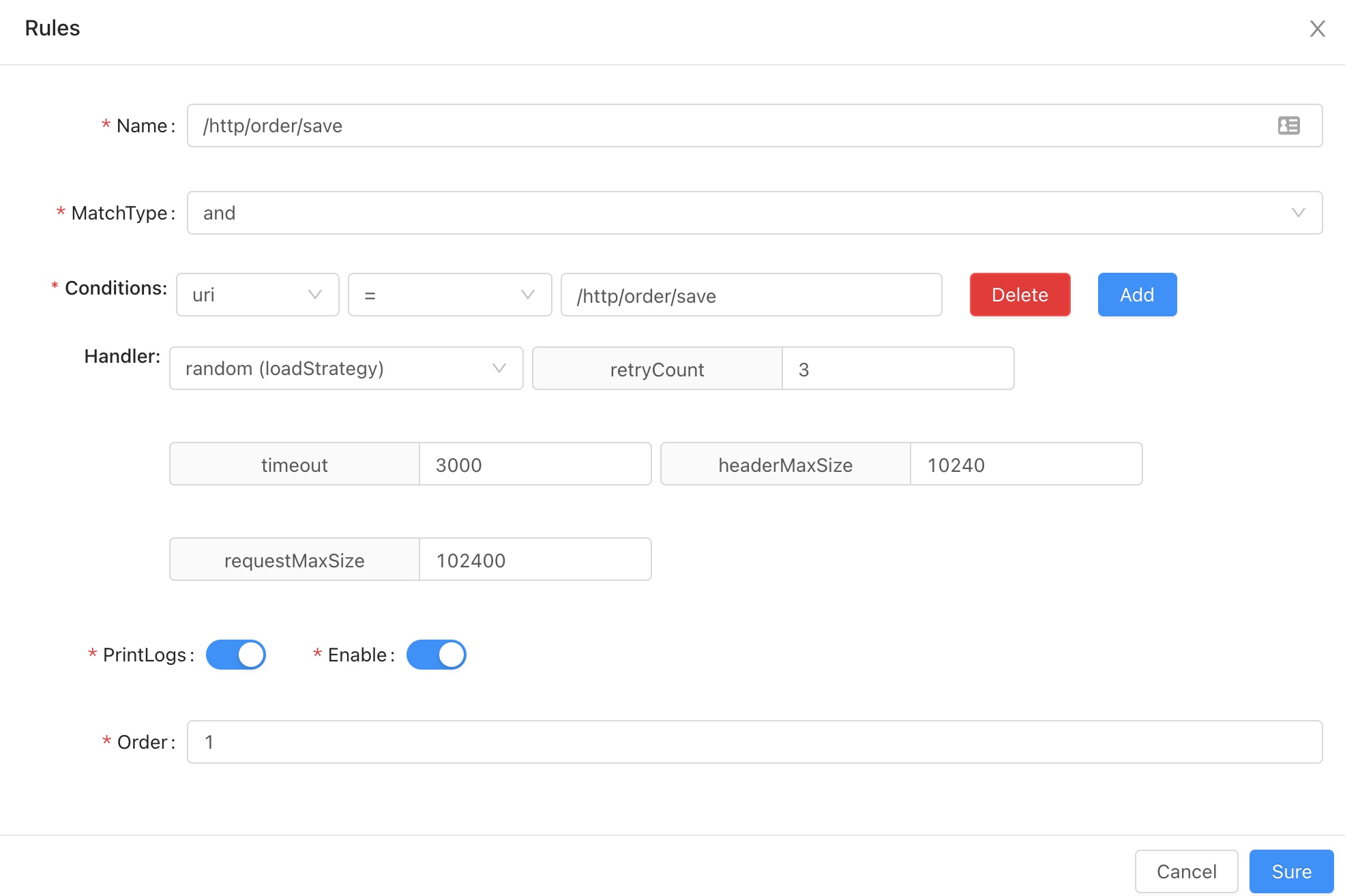
- when the request was passed by the selector, then it will be processed by the rule, the final filter.
- rule is the final confirmation about how to execute request logically.
- rule detailed explanation:
-
Name:create your rule with a distinguish name.
-
MatchType: you can combine these conditions with 'and' , 'or' operators.
-
Conditions:
-
uri: filter request with uri.
-
header: filter request with request header.
-
query: filter request with query string.
-
ip: filter request with your real ip.
-
host: filter request with your real host.
-
post: not recommend to use.
-
cookie: filter request with cookie.
-
req_method: filter request with request method.
-
condition match:
- match : fuzzy string matching,recommend to combine with uri,support path-matching.(/test/**).
- = : matches only if they are equal.
- regEx : regex matching,match characters in regex expression.
- contains: when it contains the specified value, it matches.
- TimeBefore: before the specified time.
- TimeAfter: after the specified time.
- exclude: Same function as
match, flow selection is opposite. - startsWith: when its prefix is equal to the specified value, it matches. In certain scenarios,
matchcan be replaced (such as/test/instead of/test/**) for better performance. - endsWith: when its suffix is equal to the specified value, it matches.
- pathPattern: it's an optimized version of
match, which has better performance thanmatch, but does not support writing**in the middle of the path (such as/api/**/xxx).
-
-
PrintLogs: it will print the matching log with the open option enabled.
-
Enable: whether to enable the plugin.
-
Order:the smaller will have high priority to execute among multi-rules.
-
handle: The operation when the request matches the rule.
-
- above picture means: when the request
uriequals to/http/order/save, it will execute based on this rule,load strategy israndom. - rule advice: combine
uricondition withmatchthe realuri pathcondition as the final filter. - combine selector means :when the request
uriis/http/order/save, it will be redicted to127.0.0.1:8080byrandommethod.
Match Strategy
Matching mode refers to the matching mode between multiple conditions when a selector or rule is matched. Currently, and and or are supported.
-
andandindicates that a selector or rule can be matched only if more than one condition is met.The example below shows that a request must meet both the condition
uri = /http/order/findByIdand the conditionid = 100to match this rule.For example, a real request
http://localhost:9195/http/order/findById?id=100satisfies both conditions, this rule can be matched.
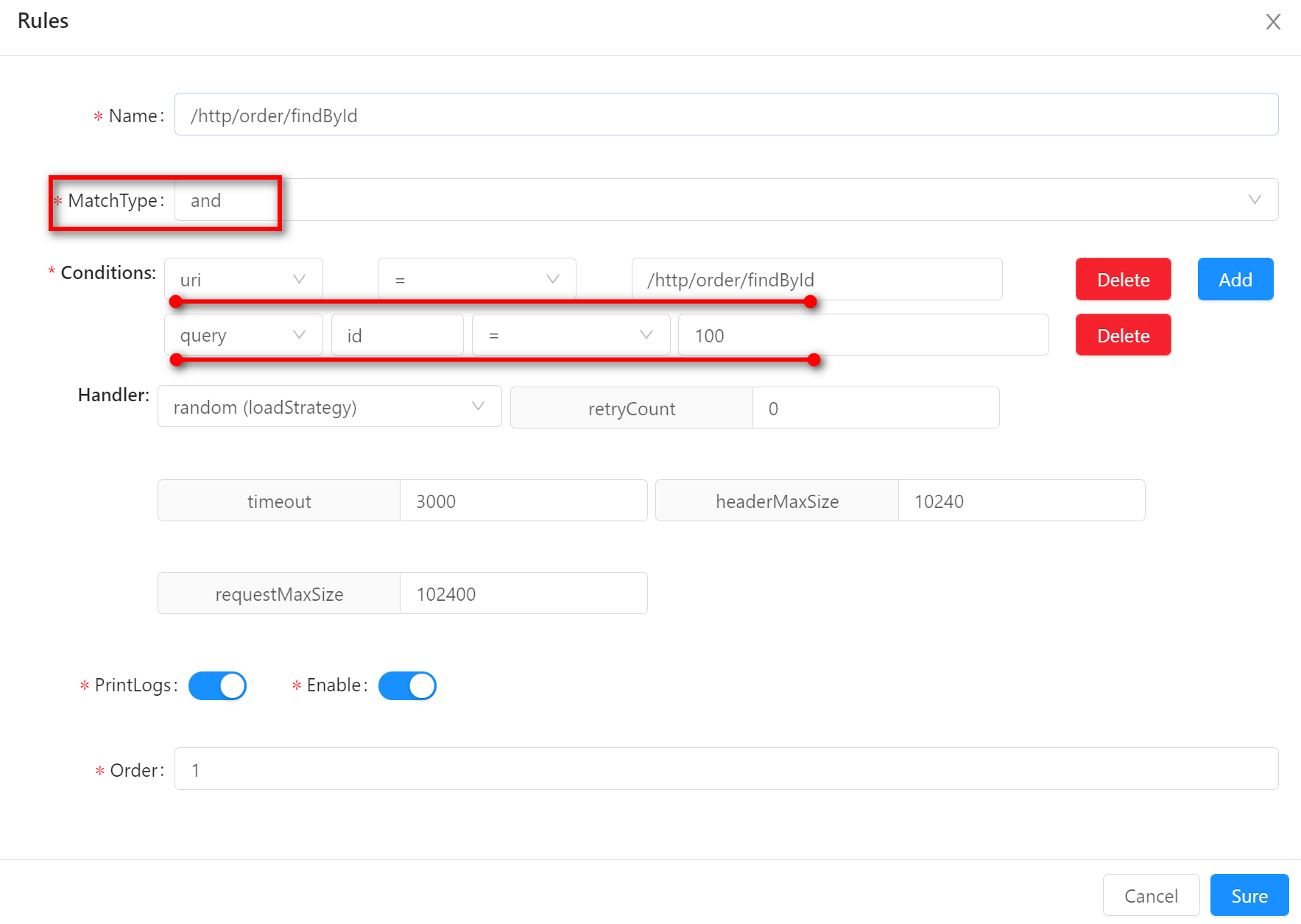
-
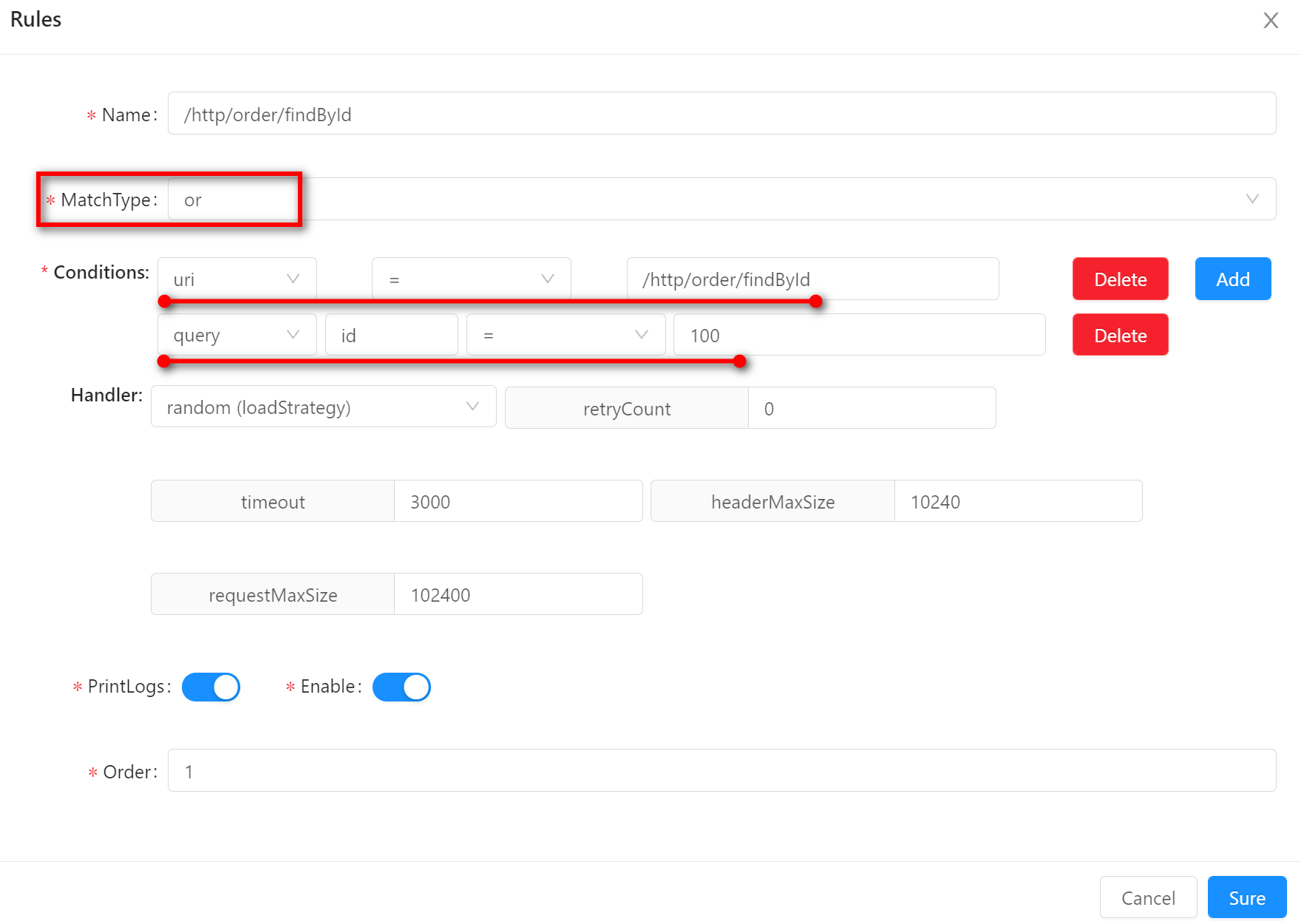
ororindicates that one of the conditions matches a selector or rule.The example below shows that a request matches this rule if it meets either the condition
uri = /http/order/findByIdor the conditionid = 100.For example, a real request
http://localhost:9195/http/order/findById?id=99satisfies the first conditionuri = /http/order/findById, so it can also match this rule.
Condition Parameter Data
Conditional parameter Settings in selectors and rules are explained again. Suppose the following is a request header for an Http request:
GET http://localhost:9195/http/order/findById?id=100
Accept: application/json
Cookie: shenyu=shenyu_cookie
MyHeader: custom-header
In ShenYu you can set different conditional parameters to get real data from the request information.
- If the condition parameter is
uri, then the actual data retrieved is/http/order/findById; - If the condition parameter is
header, the field name isMyHeader, then the actual data retrieved iscustom-header; - If the condition parameter is
query, the field name isid, then the actual data retrieved is100; - If the condition parameter is
ip, then the actual data retrieved is0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1; - If the condition parameter is
host, then the actual data retrieved is0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1; - If the condition parameter is
post, the field name iscontextPath, then the actual data retrieved is/http; - If the condition parameter is
cookie, the field name isshenyu, then the actual data retrieved isshenyu_cookie; - If the condition parameter is
req_method, then the actual data retrieved isGET;
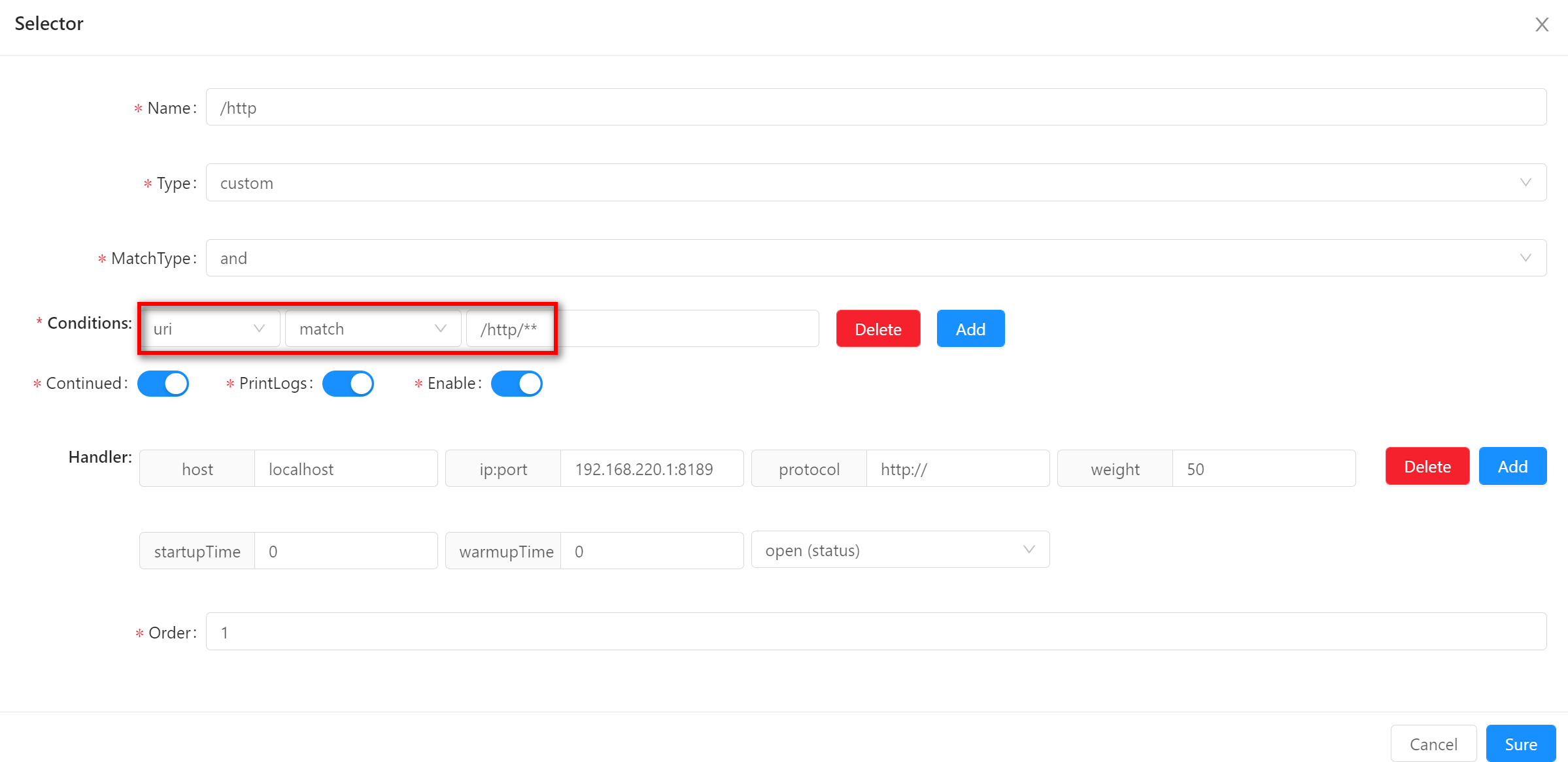
-
uri(recommended)-
urimatches are based on theuriin the path you requested, and there is almost no change in the front end when accessing the gateway. -
When using
match, the principle is the same asSpringMVCfuzzy matching. -
In selectors, it is recommended to use prefixes in
URIfor matching, while in rules, specific paths are used for matching. -
When using this matching method, fill in the value of the matching field, as shown in the figure
/http/**.
-
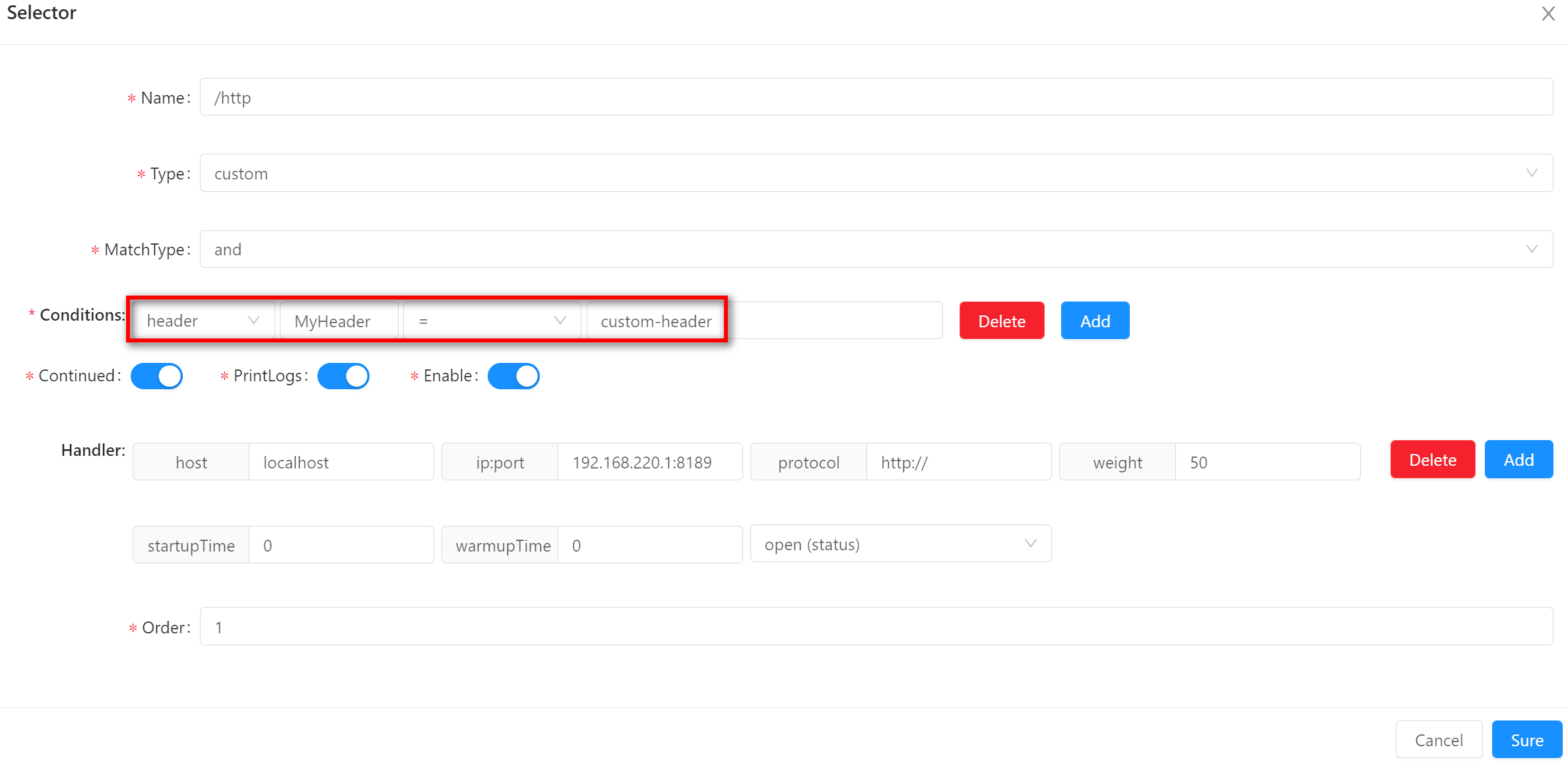
-
header-
The
headeris matched against the field values in yourhttprequest header. -
When using this matching method, you need to fill in the field name and field value. The examples in the figure are
MyHeaderandcustom-headerrespectively
-
-
query-
This matches the query parameters in your
uri, such as/test?id=1, then the matching method can be selected. -
When using this matching method, you need to fill in the field name and field value. The examples in the figure are
idand 1 respectively.
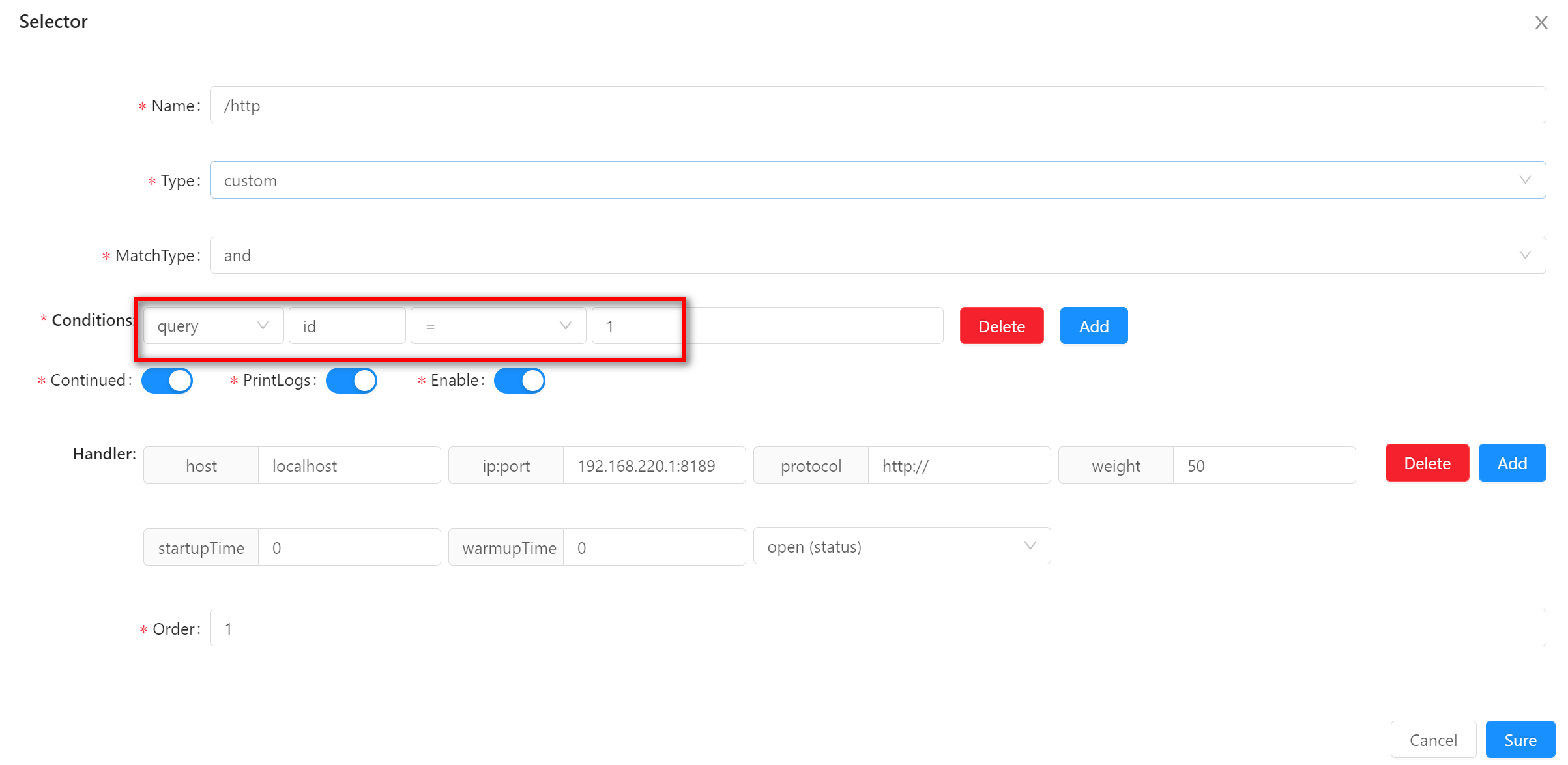
-
-
ip-
This is matched against the
httpcaller'sip. -
Especially in waf plugin, if an
ipaddress is found to be attacked, you can add a matching condition, fill in theip, deny theipaccess. -
If you use nginx proxy before ShenYu, you can get the right ip with refering to parsing-ip-and-host
-
When using this matching method, fill in the value of the matching field, as shown in the example
192.168.236.75.
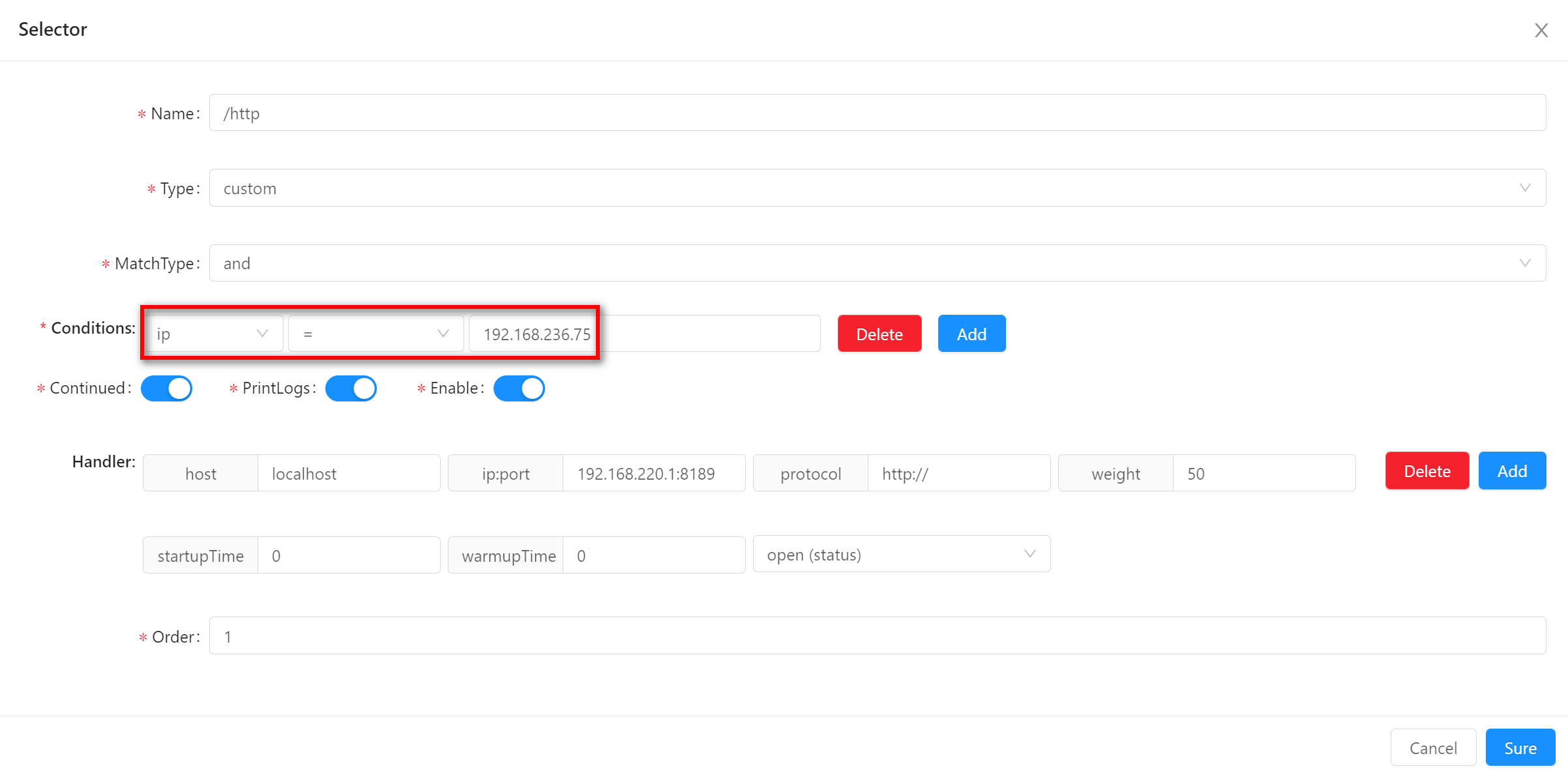
-
-
host-
This is matched against the
httpcaller'shost. -
Especially in waf plugin, if an
hostaddress is found to be attacked, you can add a matching condition, fill in thehost, deny thehostaccess. -
If you use nginx proxy before ShenYu, you can get the right ip with refering to parsing-ip-and-host
-
When using this matching method, fill in the value of the matching field, as shown in the example
localhost.
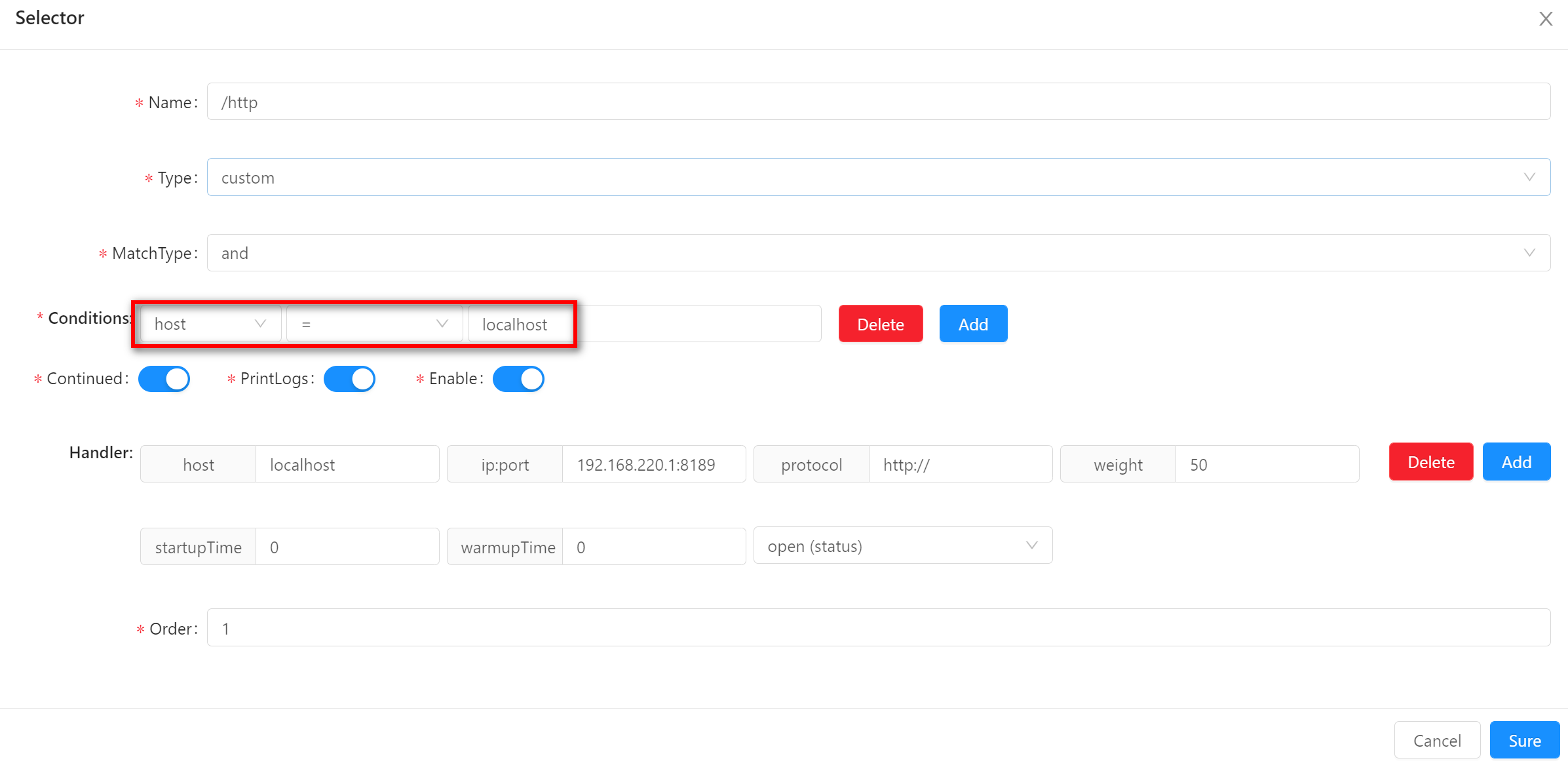
-
-
post-
To get condition parameters from the request context(
org.apache.shenyu.plugin.api.context.ShenyuContext), reflection is required to get the value of the field, which is not recommended. -
When using this matching method, the field name and value need to be specified. The examples in the figure are
contextPathand/httprespectively.
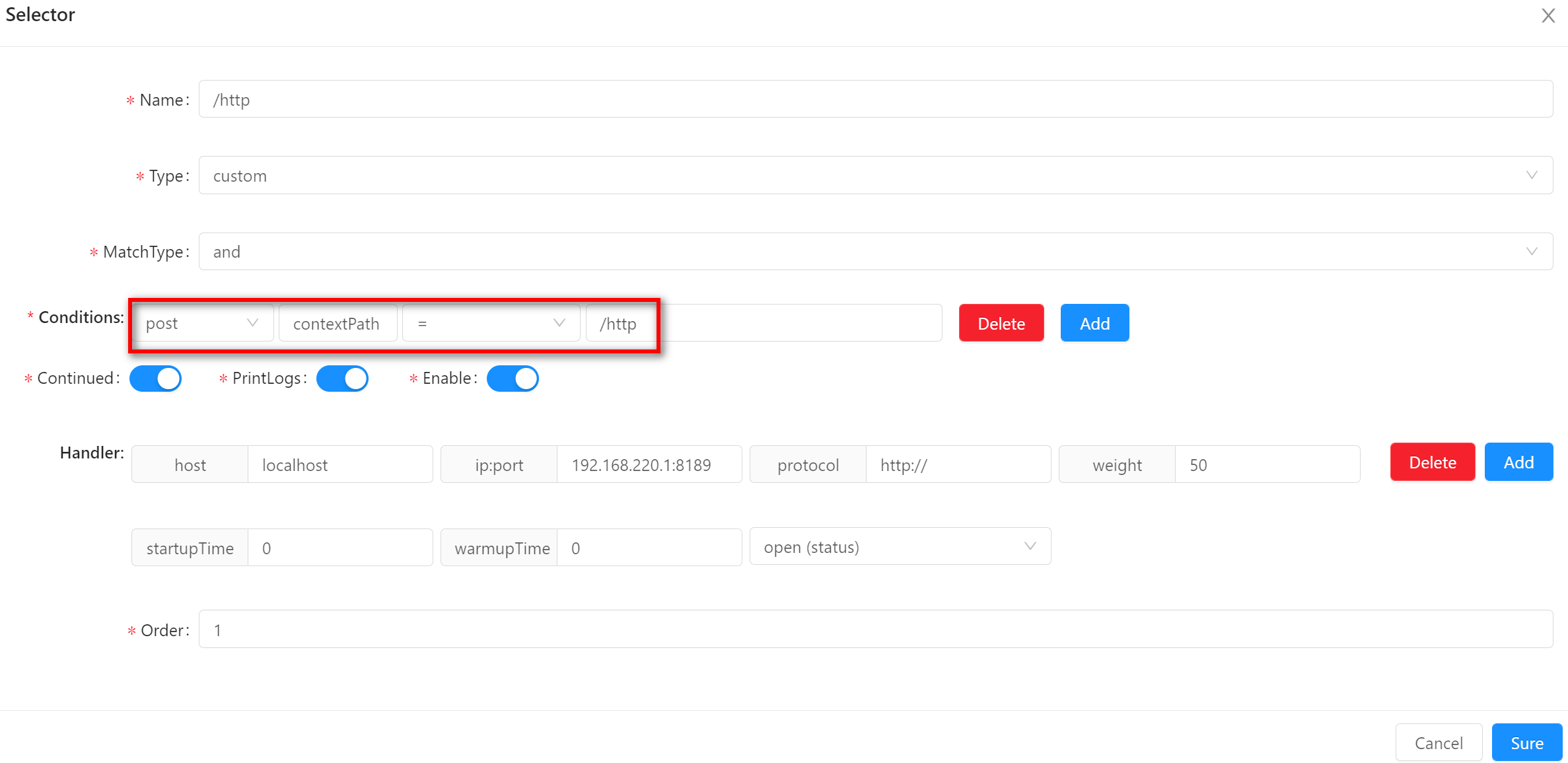
-
-
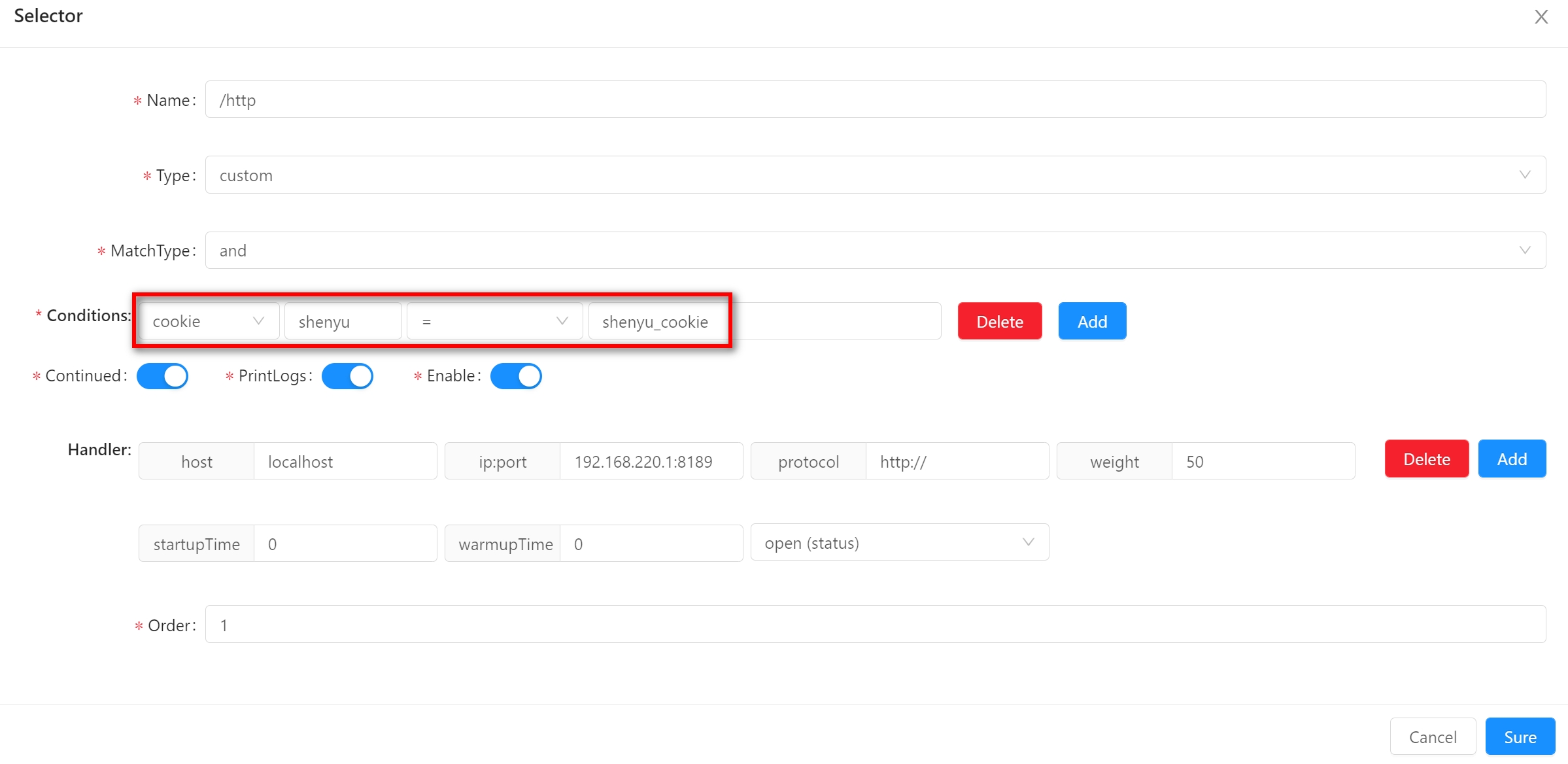
cookie-
This is matched against the
Cookiein thehttpcaller's request header as a condition parameter. -
When using this matching method, you need to fill in the field name and field value. The examples in the figure are
shenyuandshenyu_cookierespectively.
-
-
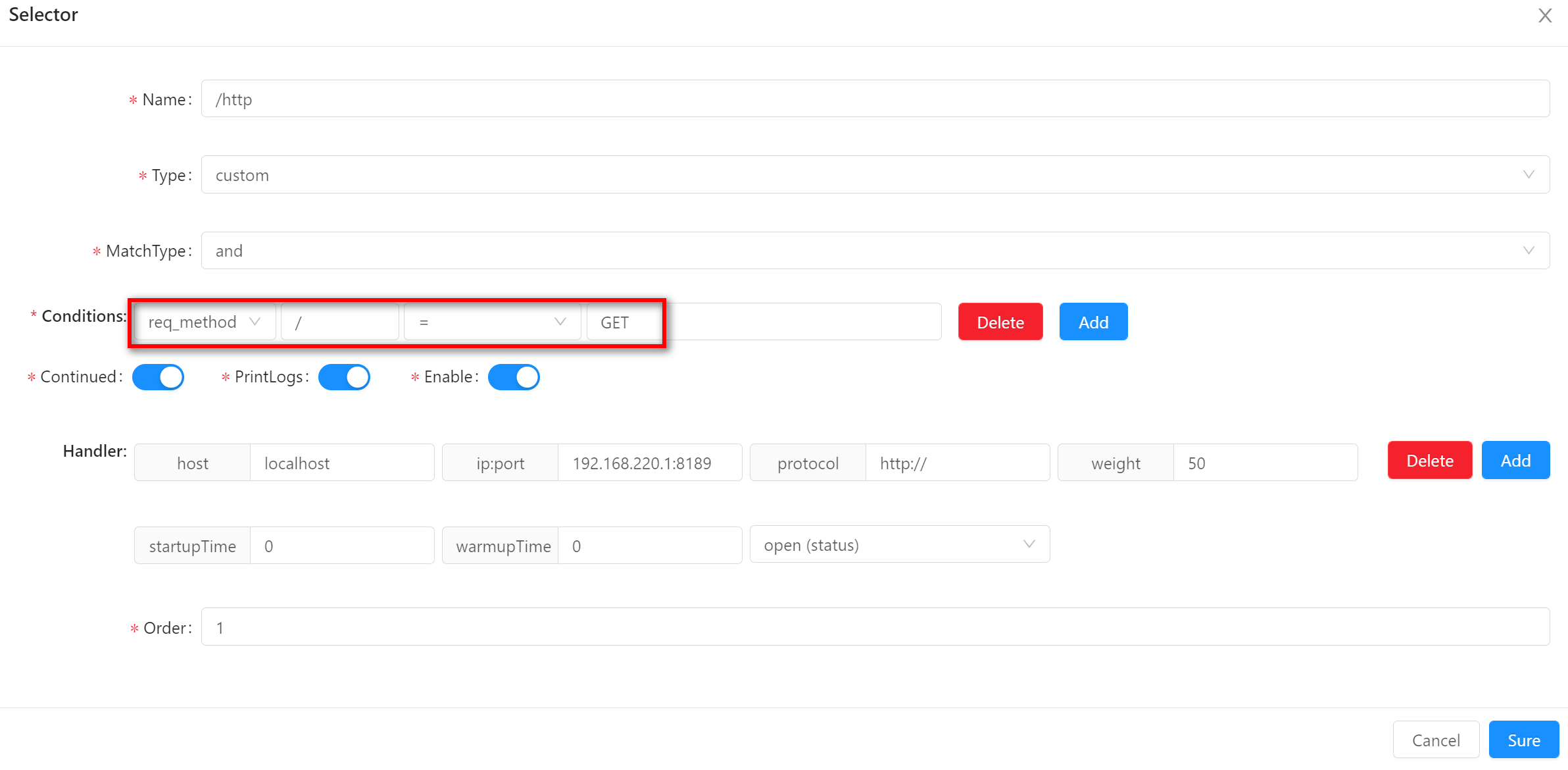
req_method-
This matches the request form of the
httpcaller, such asGET,POST, etc. -
When using this matching method, fill in the value of the matching field, as shown in the example
GET.
-
For a more in-depth understanding of condition parameter fetching, read the source code, package name is org.apache.shenyu.plugin.base.condition.data:
| Condition Parameter | Class |
|---|---|
uri | URIParameterData |
header | HeaderParameterData |
query | QueryParameterData |
ip | IpParameterData |
host | HostParameterData |
post | PostParameterData |
cookie | CookieParameterData |
req_method | RequestMethodParameterData |
Condition Match Strategy
Condition parameters allow you to retrieve the actual data of the request. How the real data matches the conditional data preset by the selector or rule is realized through the condition match strategy.
-
matchmatchsupports fuzzy matching (/**). Request/http/order/findByIdwill match if your selector condition is set as follows.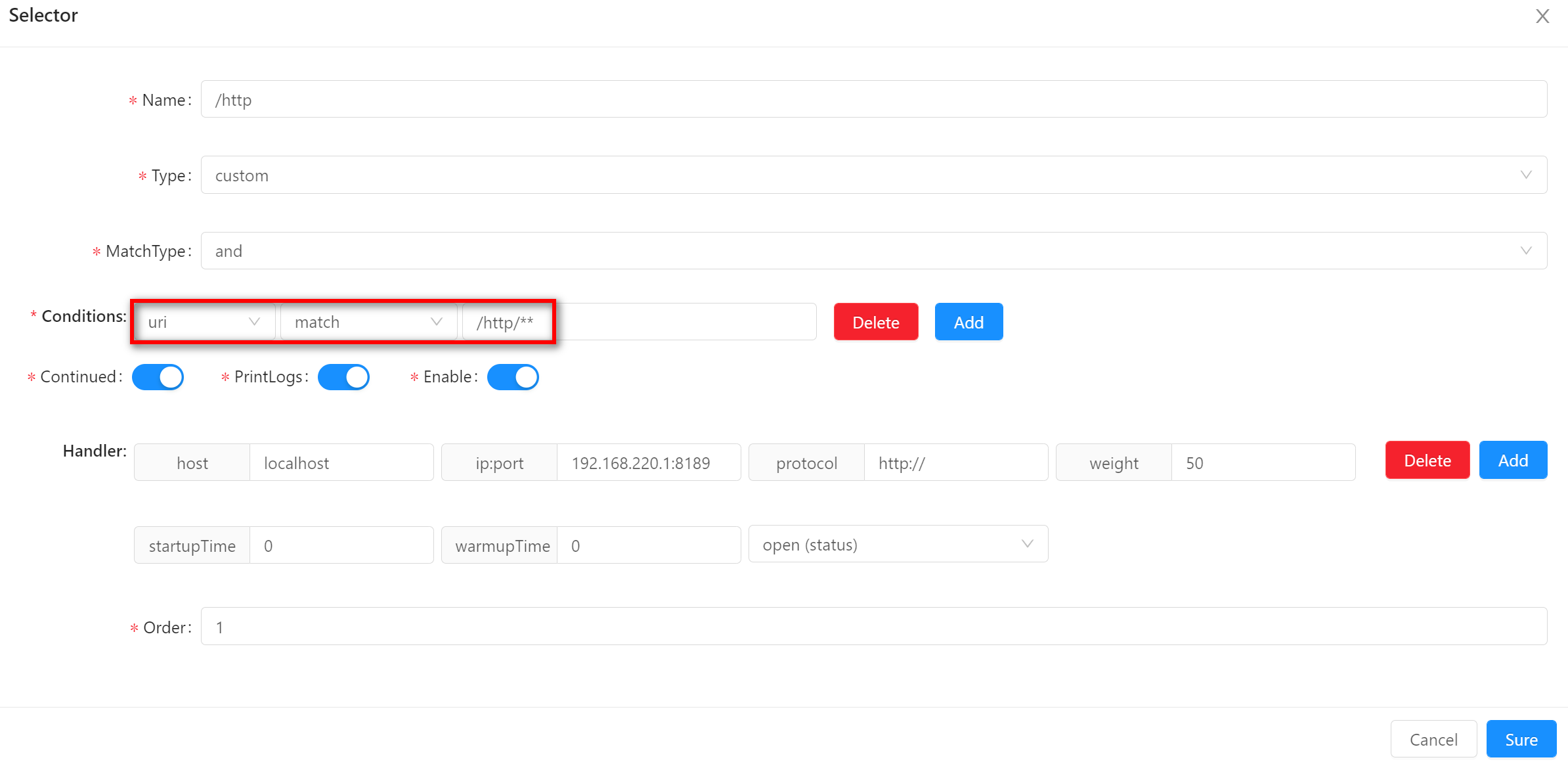
-
==means that the requested real data is equal to the preset condition data. If your selector condition is set to request uri equal to/http/order/findById, then request/http/order/findById?id=1can match it.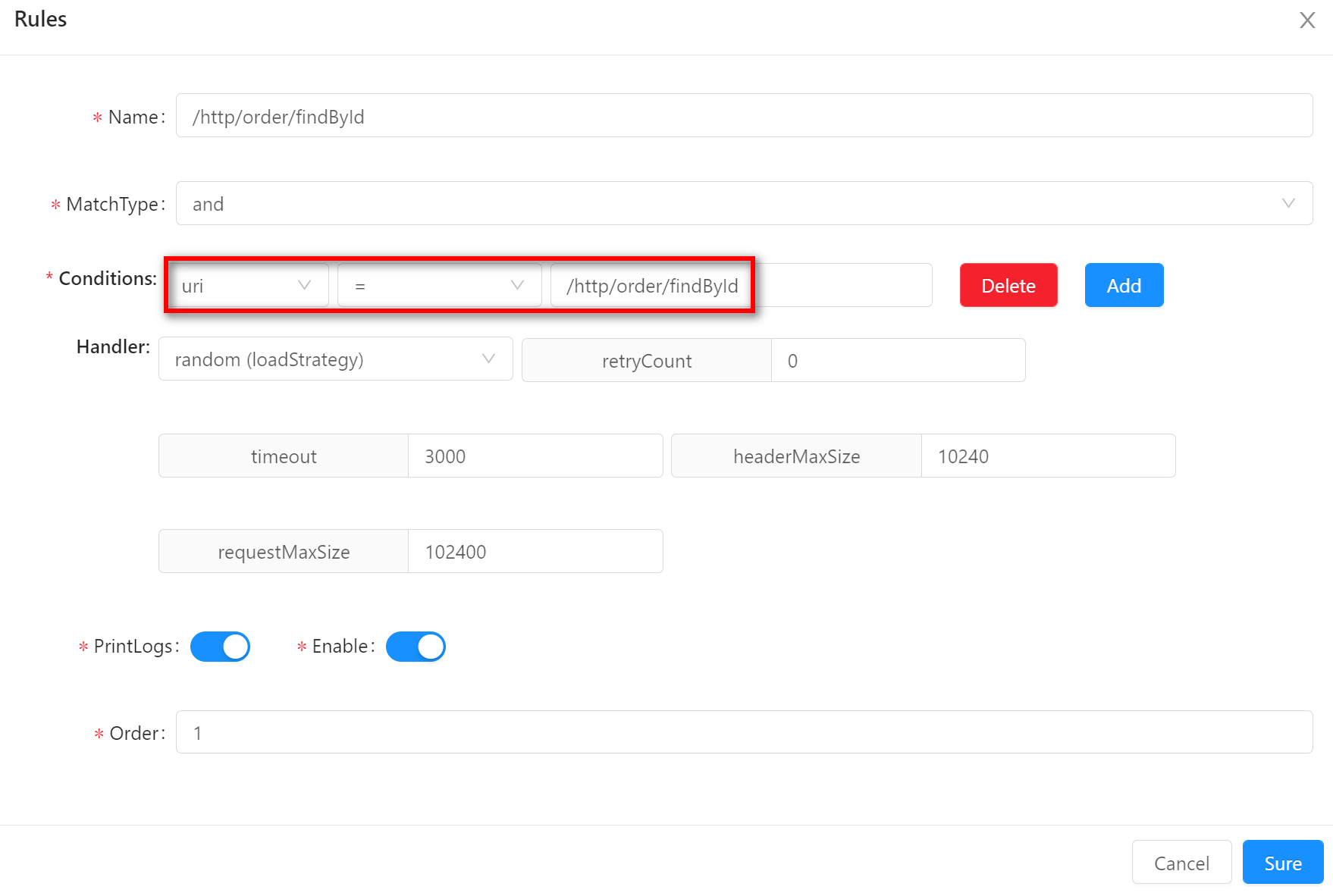
-
regexregexmeans that the requested real data can meet the preset condition of the regular expression to match successfully. Suppose your rule conditions are sets as follows: the request parameter contains anidand is a three-digit number. So request/http/order/findById?id=900will match.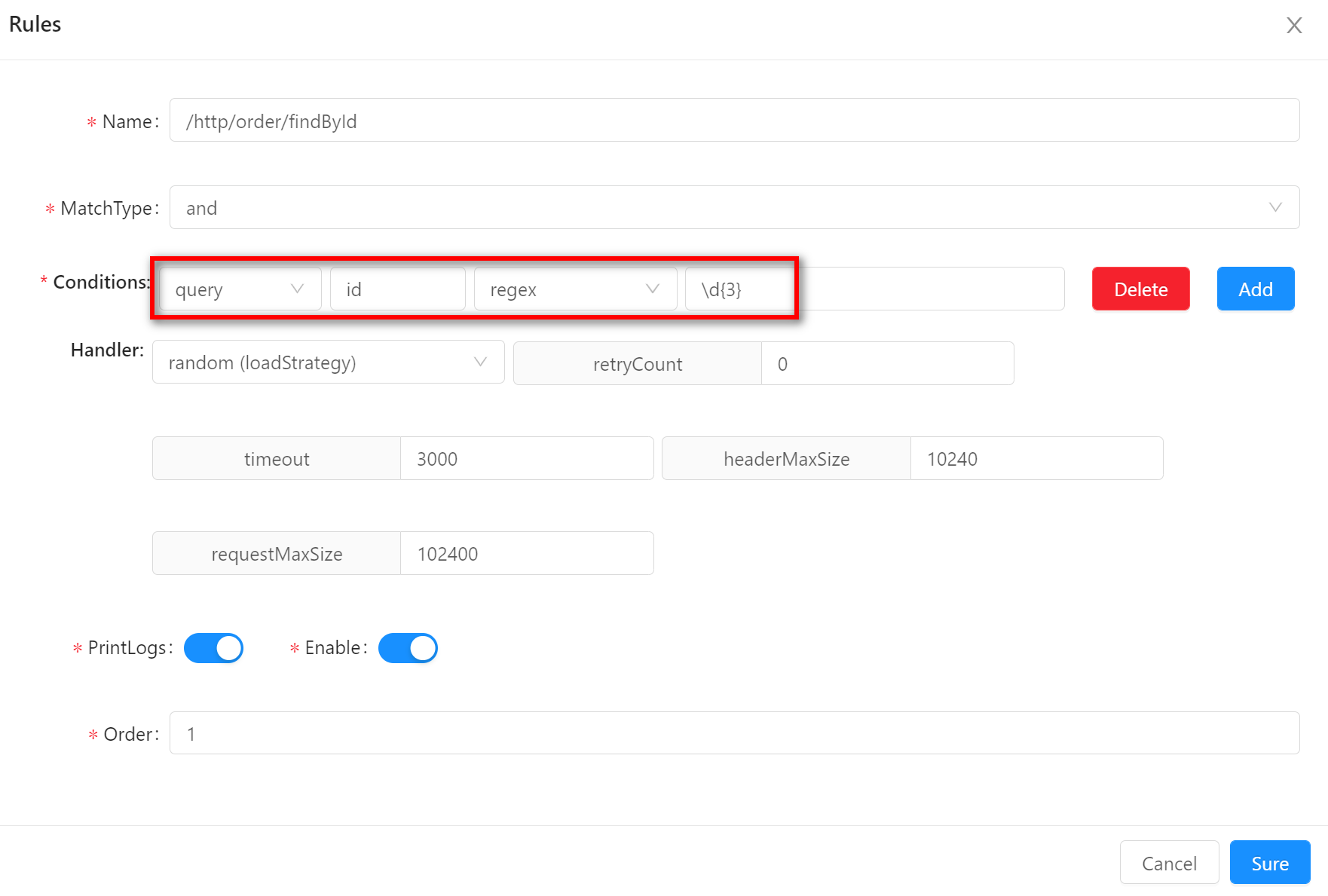
-
containscontainsmeans that the requested real data contains the default condition data. Suppose your rule condition is set as follows: request uri containsfindById. Request/http/order/findById?id=1will match.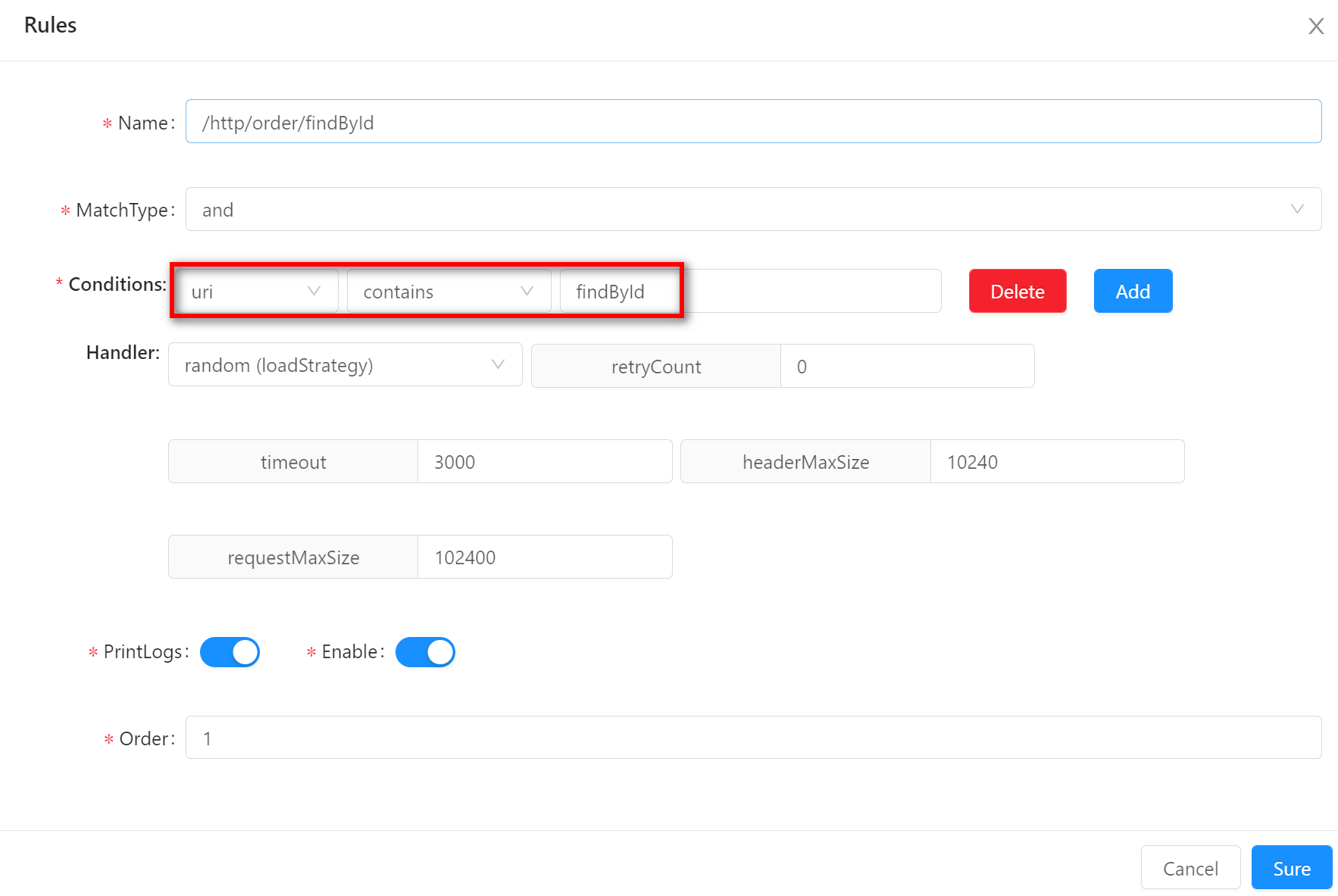
-
TimeBeforeTimeBeforeindicates that the request time will be matched before the preset condition time. Suppose your rule conditions are sets as follows: request parameters containdateanddateis less than2021-09-26 06:12:10. Request/http/order/findById?id=100&date=2021-09-22 06:12:10will match.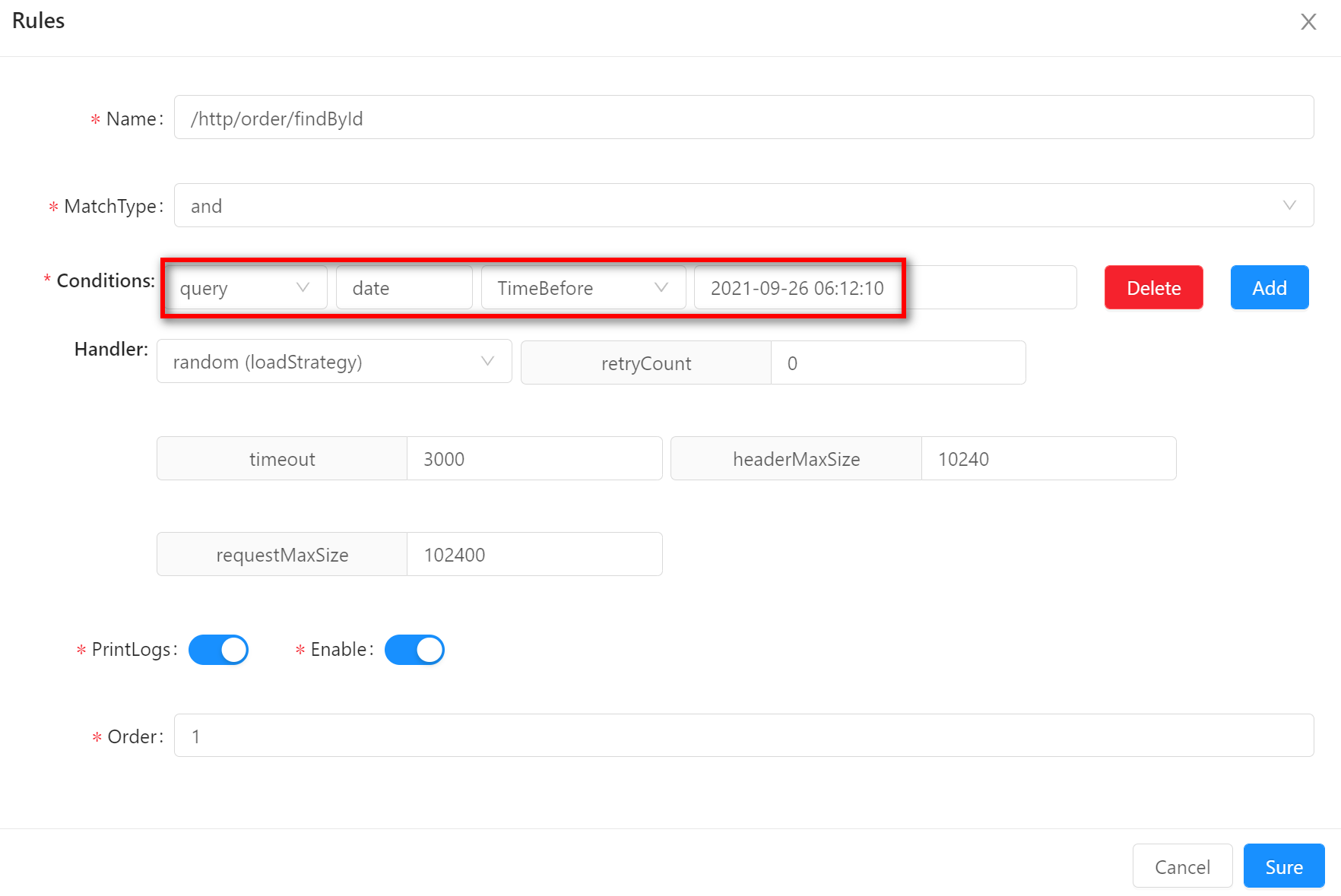
-
TimeAfterTimeAfterindicates that the request time will be matched before the preset condition time. Suppose your rule conditions are sets as follows: request parameters containdateanddateis greater than2021-09-26 06:12:10. Request/http/order/findById?id=100&date=2021-09-22 06:12:10will match.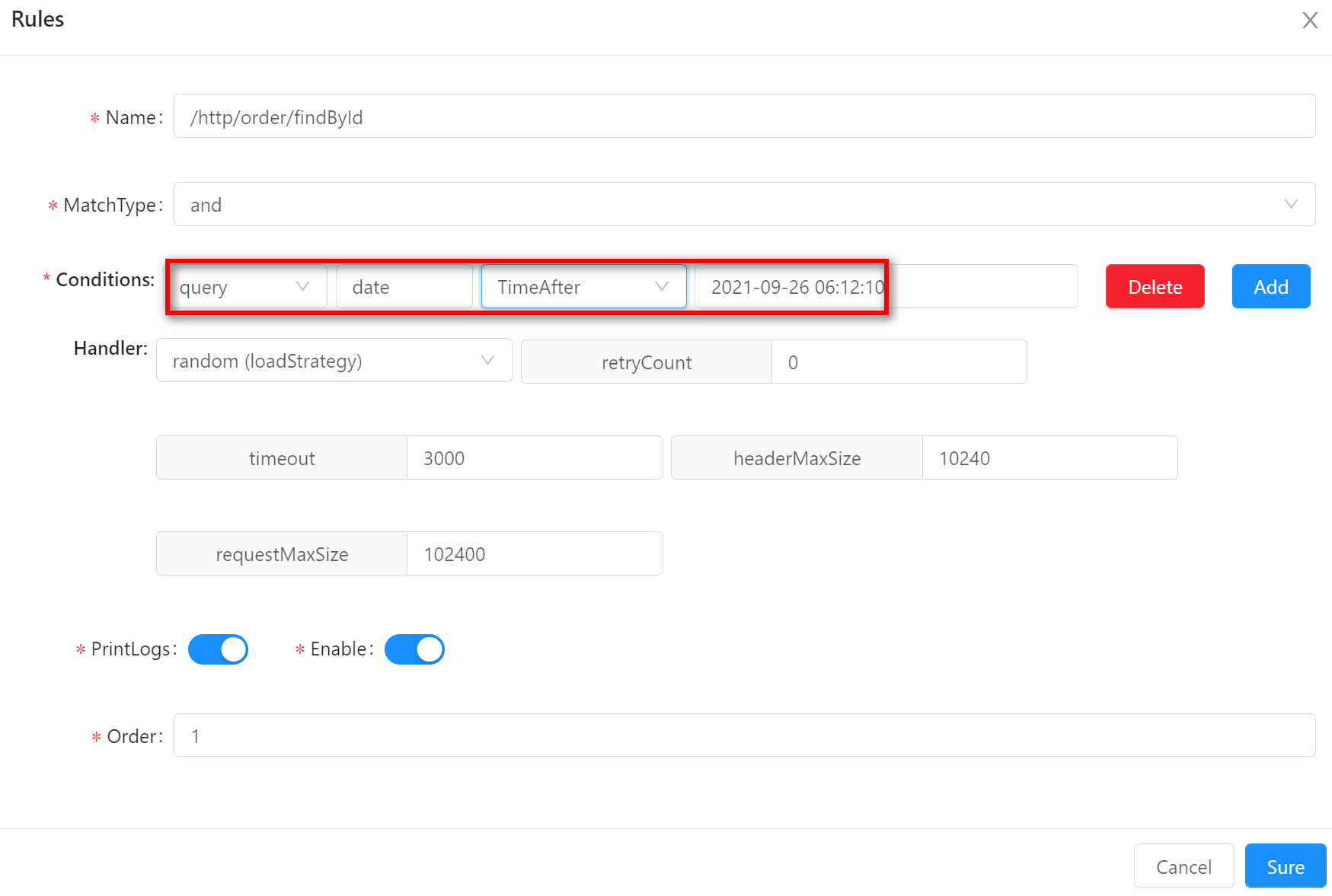
-
excludeexcludeis the inverse of the method ofmatch, and some functions ofmatchare also available, but it is a matching filter. If your selector condition is set as follows, the request/http/order/findByIdwill filter this.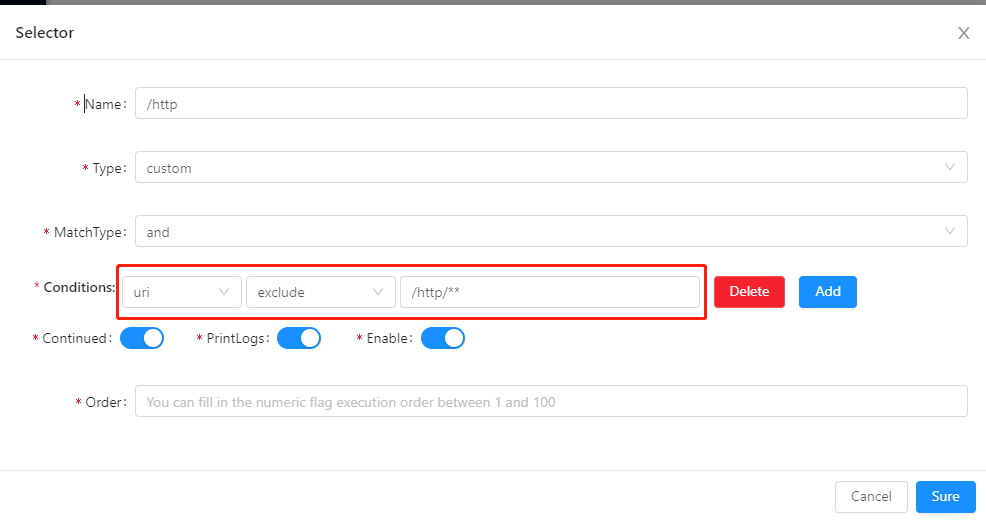
-
startsWithstartsWithindicates that the prefix of the requested real data is equal to the preset condition data. Suppose your rule conditions are sets as follows: the prefix in the requesturiis equal to/http/, the request/http/order/findById?id=1can be matched.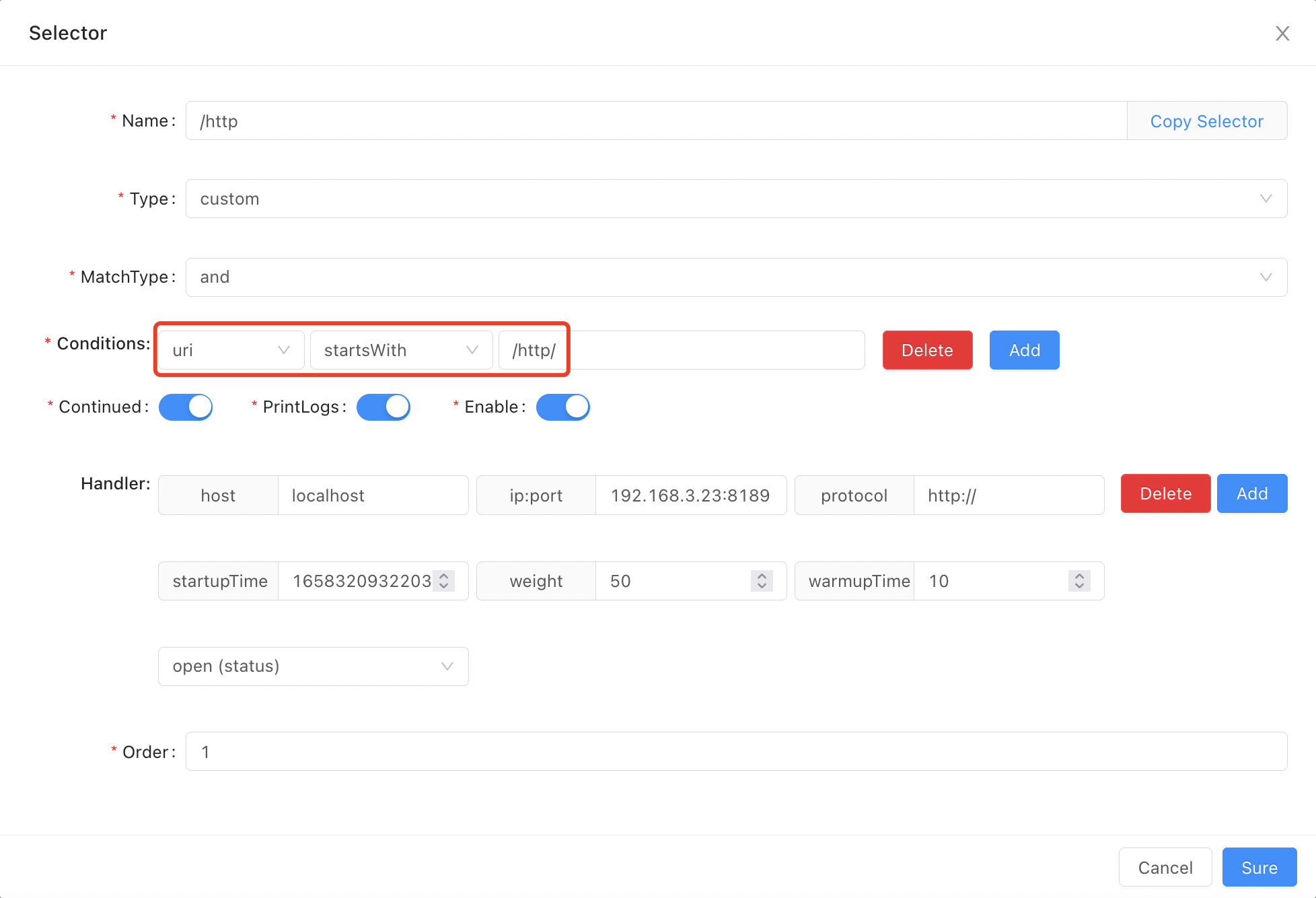
-
endsWithendsWithindicates that the suffix of the requested real data is equal to the preset condition data. Suppose your rule conditions are sets as follows: requesturisuffix equalsId. Then the request/http/order/findById?id=1can be matched.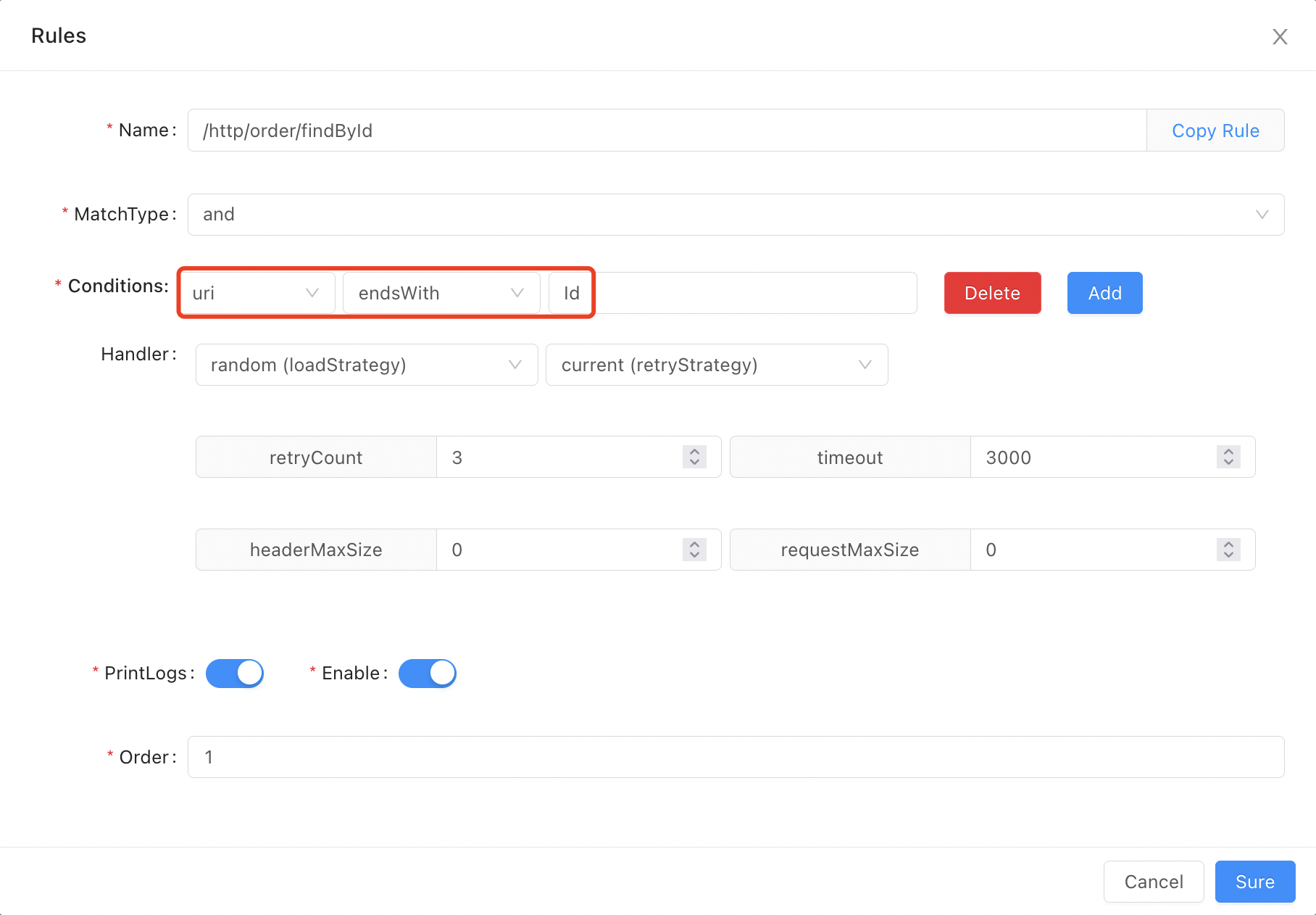
-
pathPatternLike
match,pathPatternsupports fuzzy matching (/**). If your rule conditions are sets as follows, then the request/http/order/findByIdcan be matched;Notice: writing
**in the middle of the path (such as/api/**/xxx) is not supported!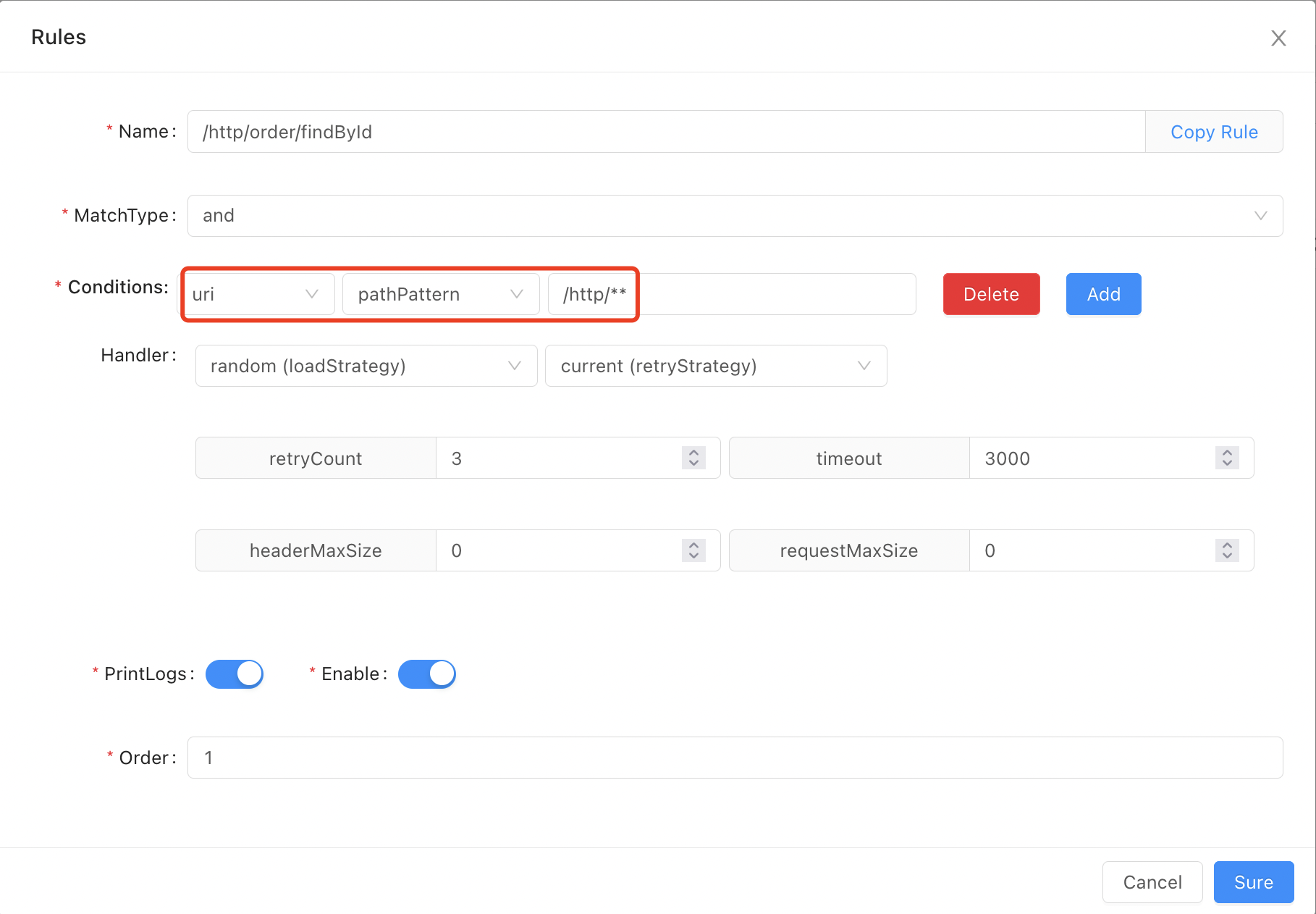
If you want to further understand conditions matching strategy, please read the source code, the package name is org.apache.shenyu.plugin.base.condition.judge:
| Match Strategy | Class |
|---|---|
match | MatchPredicateJudge |
= | EqualsPredicateJudge |
regex | RegexPredicateJudge |
contains | ContainsPredicateJudge |
TimeBefore | TimerBeforePredicateJudge |
TimeAfter | TimerAfterPredicateJudge |
exclude | ExcludePredicateJudge |
startsWith | StartsWithPredicateJudge |
endsWith | EndsWithPredicateJudge |
pathPattern | PathPatternPredicateJudge |
The examples in this article illustrate the use of selectors and rules. The Settings of specific conditions need to be selected according to actual conditions.